The eight queens puzzle in Python
Posted on November 20, 2017 by Paul
The eight queens puzzle, or the eight queens problem, asks how to place eight queens on a chessboard without attacking each other. If you never played chess before, a queen can move in any direction (horizontally, vertically and diagonally) any number of places. In the next figure, you can see two queens with their attack patterns:
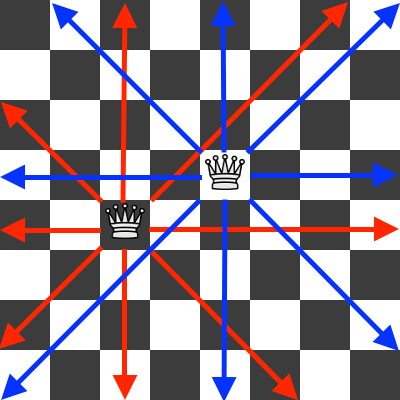
At the end of the article we present a Python 3 solution to the eight queens puzzle.
We can generate a solution to the problem by scanning each row of the board and placing one queen per column, while checking at every step, that no two queens are in the line of attack of the other. A brute force approach to the problem will be to generate all possible combinations of the eight queens on the chessboard and reject the invalid states. How many combinations of 8 queens on a 64 cells chessboard are possible ?
The combinations formula is
\[C(n,k)=_nC_k=\frac{n!}{k!\cdot(n-k)!}\]which, for our particular case is:
\[C(64,8)=_{64}C_8=\frac{64!}{8!\cdot(64-8)!}=4,426,165,368\]Clearly, the brute force approach is not practical!
We can further reduce the number of potential solutions if we observe that a valid solution can have only one queen per row, which means that we can represent the board as an array of eight elements, where each entry represents the column position of the queen from a particular row. Take as an example the next solution of the problem:
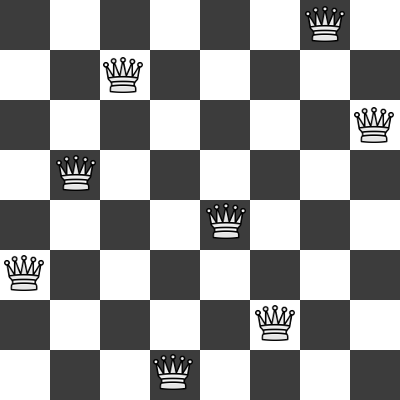
The queens positions on the above board, can be represented as the occupied positions of a two dimensional 8x8 array: [0, 6], [1, 2], [2, 7], [3, 1], [4, 4], [5, 0], [6, 5], [7, 3]. Or, as described above, we can use a one dimensional 8 elements array: [6, 2, 7, 1, 4, 0, 5, 3].
If we look closely at the example solution [6, 2, 7, 1, 4, 0, 5, 3], we note that a potential solution to the eight queens puzzle can be constructed by generating all possible permutations of an array of eight numbers, [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7], and rejecting the invalid states (the ones in which any two queens can attack each other). The number of all permutations of n unique objects is n!, which for our particular case is:
\[n!=40,320\]which is more reasonable than the previous 4,426,165,368 situations to analyze for the brute force approach.
A slightly more efficient solution to the puzzle uses a recursive approach: assume that we’ve already generated all possible ways to place k queens on the first k rows. In order to generate the valid positions for the k+1 queen we place a queen on all columns of row k+1 and we reject the invalid states. We do the above steps until all eight queens are placed on the board. This approach will generate all 92 distinct solutions for the eight queens puzzle.
Next, we present a recursive solution to the eight queens problem in Python 3. You can find the complete code on the GitHub repository for this article https://github.com/sol-prog/N-Queens-Puzzle.
1 """The n queens puzzle"""
2 class NQueens:
3 """Generate all valid solutions for the n queens puzzle"""
4 def __init__(self, size):
5 # Store the puzzle (problem) size and the number of valid solutions
6 self.size = size
7 self.solutions = 0
8 self.solve()
9
10 def solve(self):
11 """Solve the n queens puzzle and print the number of solutions"""
12 positions = [-1] * self.size
13 self.put_queen(positions, 0)
14 print("Found", self.solutions, "solutions.")
15
16 def put_queen(self, positions, target_row):
17 """
18 Try to place a queen on target_row by checking all N possible cases.
19 If a valid place is found the function calls itself trying to place a queen
20 on the next row until all N queens are placed on the NxN board.
21 """
22 # Base (stop) case - all N rows are occupied
23 if target_row == self.size:
24 self.show_full_board(positions)
25 self.solutions += 1
26 else:
27 # For all N columns positions try to place a queen
28 for column in range(self.size):
29 # Reject all invalid positions
30 if self.check_place(positions, target_row, column):
31 positions[target_row] = column
32 self.put_queen(positions, target_row + 1)
33
34 def check_place(self, positions, ocuppied_rows, column):
35 """
36 Check if a given position is under attack from any of
37 the previously placed queens (check column and diagonal positions)
38 """
39 for i in range(ocuppied_rows):
40 if positions[i] == column or \
41 positions[i] - i == column - ocuppied_rows or \
42 positions[i] + i == column + ocuppied_rows:
43
44 return False
45 return True
46
47 def show_full_board(self, positions):
48 """Show the full NxN board"""
49 for row in range(self.size):
50 line = ""
51 for column in range(self.size):
52 if positions[row] == column:
53 line += "Q "
54 else:
55 line += ". "
56 print(line)
57 print("\n")
58
59 def main():
60 """Initialize and solve the n queens puzzle"""
61 NQueens(8)
62
63 if __name__ == "__main__":
64 # execute only if run as a script
65 main()Here is the result of running the above code in a Python REPL for a 4x4 board:
1 >>> from nqueens import NQueens
2 >>> _ = NQueens(4)
3 . Q . .
4 . . . Q
5 Q . . .
6 . . Q .
7
8
9 . . Q .
10 Q . . .
11 . . . Q
12 . Q . .
13
14
15 Found 2 solutions.
16 >>>You can further enhance the implementation by adding a GUI that will let you better visualize the solutions. A possible approach is to use the tkinter module which is already included with your Python installation.
If you want to learn more about Python, I recommend reading Python Crash Course by Eric Matthes:
